Summary
Free flow electrophoresis was employed to separate renal cortical plasma membranes into luminal (brush border microvilli) and contraluminal (basal-lateral membrane) fractions. During the separation adenylate cyclase activity was found to parallel the activity of Na+−K+-activated ATPase, an enzyme which is present in contraluminal but not in luminal membranes. In the basal-lateral membrane fraction the specific activities of adenylate cyclase and Na+−K+-activated ATPase were 4.4 and 4.6 times greater, respectively, than in the brush border fraction.
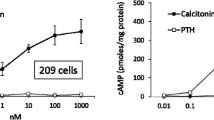
The adenylate cyclase of the basal-lateral membrane fraction was specifically stimulated by parathyroid hormone which maximally increased enzyme activity eightfold. The biologically active (1–34) peptide fragment of parathyroid hormone produced a 350% increase in adenylate cyclase activity. In contrast, calcitonin, epinephrine and vasopressin maximally stimulated the enzyme by only 55, 35 and 30%, respectively.
These results indicate that adenylate cyclase, specifically stimulated by parathyroid hormone, is distributed preferentially in the contraluminal region of the plasma membrane of renal cortical epithelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agus, Z.S., Gardner, L.B., Beck, L.H., Goldberg, M. 1973. Effects of parathyroid hormone on renal tubular reabsorption of calcium, sodium, and phosphate.Am. J. Physiol. 224:1143
Agus, Z.S., Puschett, J.B., Senesky, D., Goldberg, M. 1971. Mode of action of parathyroid hormone and cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate on renal tubular phosphate reabsorption in the dog.J. Clin. Invest. 50:617
Bär, H.-P., Hechter, O. 1969. Adenyl cylase assy in fat cell ghosts.Anal. Biochem. 29:476
Chase, L.R., Aurbach, G.D. 1967. Parathyroid function and the renal excretion of 3′,5′-adenylic acid.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 58:518
Chase, L.R., Aurbach, G.D. 1968. Renal adenyl cyclase: Anatomically separate sites for parathyroid hormone and vasopressin.Science 159:545
DiBella, F.P., Dousa, T.P., Miller, S.S., Arnaud, C.D. 1974. Parathyroid hormone receptors of renal cortex: Specific binding of biologically active,125I-labeled hormone and relationship to adenylate cyclase activation.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 71:723
Ericsson, J.L.E., Trump, B.F. 1969. Electron microscopy of the uriniferous tubules.In: The Kidney. C. Rouiller and A.F. Muller, editors. Vol. 1, p. 351. Academic Press, New York
Forte, L.R. 1972. Characterization of the adenyl cyclase of rat kidney plasma membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 266:524
Grantham, J.J., Burg, M.B. 1966. Effect of vasopressin and cyclic AMP on permeability of isolated collecting tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 211:255
Györy, A.Z., Kinne, R. 1971. Energy source for transepithelial sodium transport in rat renal proximal tubules.Pflügers Arch. 327:234
Hannig, K. 1968. Die Ablenkungselektrophorese. Handbuch der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft, Munich, 116
Heidrich, H.G., Kinne, R., Kinne-Saffran, E., Hannig, K. 1972. The polarity of the proximal tubule cell in rat kidney.J. Cell Biol. 54:232
Kinne, R., Kinne-Saffran, E. 1969. Isolierung und enzymatische Charakterisierung einer Bürstensaumfraktion der Rattenniere.Pflügers Arch. 308:1
Kinne, R., Schmitz, J.E., Kinne-Saffran, E. 1971. The localization of the Na+−K+-ATPase in the cells of rat kidney cortex: A study on isolated plasma membranes.Pflügers Arch. 329:191
Kinne, R., Shlatz, L.J., Kinne-Saffran, E., Schwartz, I.L. 1975. Distribution of membrane-bound cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in plasma membranes of cells of the kidney cortex.J. Membr. Biol. 24:145
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, H.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193:265
Marcus, R., Aurbach, G.D. 1971. Adenyl cyclase from renal cortex.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 242:410
Marx, S.J., Fedak, S.A., Aurbach, G.D. 1972a. Preparation and characterization of a hormone-responsive renal plasma membrane fraction.J. Biol. Chem. 247:6913
Marx, S.J., Woodward, C.J., Aurbach, G.D. 1972b. Calcitonin receptors of kidney and bone.Science 178:999
Marx, S.J., Woodward, C.J., Aurbach, G.D., Glossman, H., Keutmann, H.T. 1973. Renal receptors for calcitonin.J. Biol. Chem. 248:4797
Melson, G.L., Chase, L.R., Aurbach, G.D. 1970. Parathyroid hormone-sensitive adenyl cyclase in isolated renal tubules.Endocrinology 86:511
Molbert, E.F.G., Duspiva, F., Von Deimling, O.H. 1960. The demonstration of alkaline phosphatase in the electron microscope.J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 7:387
Pockrandt-Hemstedt, H., Schmitz, J.E., Kinne-Saffran, E., Kinne, R. 1972. Morphologische und biochemische Untersuchungen über die Oberflächenstruktur der Bürstensaummembran der Rattenniere. (Surface structure of isolated brushborder of rat kidney: Morphological and biochemical analysis.)Pflügers Arch. 333:297
Ray, T.K. 1970. A modified method for the isolation of the plasma membrane from rat liver.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 196:1
Samiy, A.H., Hirsch, P.F., Ramsay, A.G. 1965. Localization of phosphaturic effect of parathyroid hormone in nephron of the dog.Am. J. Physiol. 208:73
Schmidt, U., Dubach, U.C. 1971. Na K stimulated adenosinetriphosphatase: Intracellular localization within the proximal tubule of the rat nephron.Pflügers Arch. 330:265
Shlatz, L.J., Schwartz, I.L. 1972. Studies on the adenyl cyclase of rat renal cortical and medullary plasma membranes.Physiologist 15:265
Sutcliffe, H.S., Martin, T.J., Eisman, J.A., Pilczyk, R. 1973. Binding of parathyroid hormone to bovine kidney-cortex plasma membranes.Biochem. J. 134:913
Talmage, R.V., Kraintz, F.W. 1954. Progressive changes in renal phosphate and calcium excretion in rats following parathyroidectomy or parathyroid administration.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 87:263
Wilfong, R.F., Neville, D.M., Jr. 1970. The isolation of a brush border membrane fraction from rat kidney.J. Biol. Chem. 245:6106
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shlatz, L.J., Schwartz, I.L., Kinne-Saffran, E. et al. Distribution of parathyroid hormone-stimulated adenylate cyclase in plasma membranes of cells of the kidney cortex. J. Membrain Biol. 24, 131–144 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868619
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868619